'방문 길이' 정의는 다음과 같다.
게임 캐릭터를 4가지 명령어를 통해 움직이려 합니다. 명령어는 다음과 같습니다.
- U: 위쪽으로 한 칸 가기
- D: 아래쪽으로 한 칸 가기
- R: 오른쪽으로 한 칸 가기
- L: 왼쪽으로 한 칸 가기
캐릭터는 좌표평면의 (0, 0) 위치에서 시작합니다. 좌표평면의 경계는 왼쪽 위(-5, 5), 왼쪽 아래(-5, -5), 오른쪽 위(5, 5), 오른쪽 아래(5, -5)로 이루어져 있습니다.

예를 들어, ULURRDLLU로 명령했다면

- 1번 명령어부터 7번 명령어까지 다음과 같이 움직입니다.

- 8번 명령어부터 9번 명령어까지 다음과 같이 움직입니다.
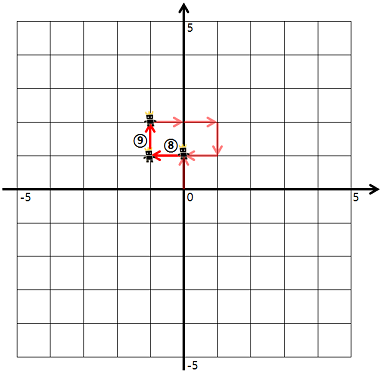
이때, 우리는 게임 캐릭터가 지나간 길 중 캐릭터가 처음 걸어본 길의 길이를 구하려고 합니다. 예를 들어 위의 예시에서 게임 캐릭터가 움직인 길이는 9이지만, 캐릭터가 처음 걸어본 길의 길이는 7이 됩니다. (8, 9번 명령어에서 움직인 길은 2, 3번 명령어에서 이미 거쳐 간 길입니다)
단, 좌표평면의 경계를 넘어가는 명령어는 무시합니다.
예를 들어, LULLLLLLU로 명령했다면

- 1번 명령어부터 6번 명령어대로 움직인 후, 7, 8번 명령어는 무시합니다. 다시 9번 명령어대로 움직입니다.

이때 캐릭터가 처음 걸어본 길의 길이는 7이 됩니다.
명령어가 매개변수 dirs로 주어질 때, 게임 캐릭터가 처음 걸어본 길의 길이를 구하여 return 하는 solution 함수를 완성해 주세요.
제한사항
- dirs는 string형으로 주어지며, 'U', 'D', 'R', 'L' 이외에 문자는 주어지지 않습니다.
- dirs의 길이는 500 이하의 자연수입니다.
입출력 예
| dirs | answer |
| ULURRDLLU | 7 |
| LULLLLLLU | 7 |
다음과 같이 코드를 작성했다.
class Location {
private boolean left;
private boolean right;
private boolean up;
private boolean down;
public void setLeft(boolean left) {
this.left = left;
}
public void setRight(boolean right) {
this.right = right;
}
public void setUp(boolean up) {
this.up = up;
}
public void setDown(boolean down) {
this.down = down;
}
public boolean getLeft() {
return left;
}
public boolean getRight() {
return right;
}
public boolean getUp() {
return up;
}
public boolean getDown() {
return down;
}
}
class Solution {
private static int boundary = 5;
public int solution(String dirs) {
if (dirs.length() > 500) {
System.out.println("입력 길이 초과 오류");
return -1;
}
int answer = 0;
int center = boundary;
int x = center;
int y = center;
int max = boundary * 2;
// 위치 정보 객체 배열 생성
Location[][] location = new Location[max + 1][max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < location.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < location[i].length; j++) {
location[i][j] = new Location();
}
}
// 방문 길이 연산
for (int i = 0; i < dirs.length(); i++) {
char move = dirs.charAt(i);
switch (move) {
case 'U':
if (y < max) {
if (!location[x][y].getUp()) {
answer++;
}
location[x][y].setUp(true);
y++;
location[x][y].setDown(true);
}
break;
case 'R':
if (x < max) {
if (!location[x][y].getRight()) {
answer++;
}
location[x][y].setRight(true);
x++;
location[x][y].setLeft(true);
}
break;
case 'L':
if (x > 0) {
if (!location[x][y].getLeft()) {
answer++;
}
location[x][y].setLeft(true);
x--;
location[x][y].setRight(true);
}
break;
case 'D':
if (y > 0) {
if (!location[x][y].getDown()) {
answer++;
}
location[x][y].setDown(true);
y--;
location[x][y].setUp(true);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return answer;
}
}1. 상, 하, 좌, 우 길의 방문 여부를 필드를 가진 Location 객체를 원소로 2차원 배열을 생성한다.
2. charAt() 메소드를 이용하여 입력된 스트링 dirs에서 각 문자를 추출한다.
3. 조건 분기를 통해 방문 길을 검증한다.
charAt()을 사용했지만, 다음과 같이 split("")을 사용할 수도 있다.
// use charAt(idx)
for (int i = 0; i < dirs.length(); i++) {
char move = dirs.charAt(i);
}
// use split("")
for (String dir : dirs.split("")) {
}Location 객체만 이용했기 때문에 뭔가 solution()의 코드가 절차적으로 보인다.
Character 객체를 따로 만들어 분리하는 것도 좋은 방법일 것 같다.
'Coding Test > Others' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm] 소수 만들기 (0) | 2020.11.10 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] 영어 끝말잇기 (1) | 2020.10.15 |
| [Algorithm] 수포자 (0) | 2020.10.14 |
| [Algorithm] 다음 큰 숫자 (0) | 2020.08.24 |
| [Algorithm] 하샤드 수 (0) | 2020.08.16 |